How does a VMC work?
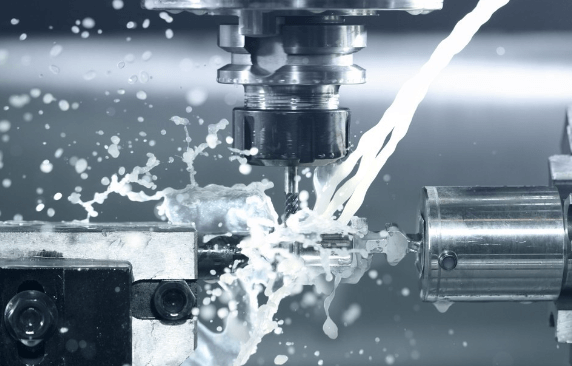
Introduction to VMC
A Vertical Machining Center (VMC) is a critical tool in modern manufacturing environments, offering the capability to perform milling, drilling, and tapping operations. These machines are characterized by their vertical orientation of the spindle where tools spin while the workpiece is mounted on a stationary bed. This design allows gravity to assist with the removal of metal chips, making it ideal for heavy-duty cutting tasks.
Components of a VMC
A VMC comprises several key components that work together to execute precise machining tasks:
- Structure and Frame: The robust frame supports all the machine’s components and ensures stability during heavy operations.
- The Spindle: Heart of the VMC: The spindle holds the tool and is responsible for its rotation at high speeds.
- Tool Magazine and Tool Changer: These elements allow the machine to hold multiple tools and switch between them automatically, minimizing downtime.
- Control Panel: The Brain of VMC: This is where operators input commands and parameters, guiding the machine’s operations through CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology.
Types of VMCs
VMCs come in various configurations to meet different production needs:
- Standard Vertical Machining Centers are suited for a range of general manufacturing tasks.
- Advanced High-Speed VMCs offer greater speed and precision, ideal for complex parts.
- Specialty VMCs for Unique Applications are customized for specific industries like aerospace and automotive, where unique materials and precision are crucial.
How Does a VMC Operate?
The Operational Workflow of a VMC
Operating a VMC involves several steps that ensure efficient and accurate machining:
- Setting Up the Machine: This includes configuring the machine with the right tools and materials.
- Tool Loading and Tool Change Process: Tools are loaded into the magazine, and the machine automatically switches them as needed.
- The Machining Process: The machine uses programmed instructions to mill, drill, or tap, transforming a raw piece into a finished part.
CNC Technology in VMCs
CNC plays a pivotal role in a VMC’s operation:
- Role of CNC in Enhancing VMC Performance: CNC systems provide precise control over the machining process, allowing for complex shapes and high-quality finishes.
- Programming CNC for Optimal Machining: Detailed programming is crucial for maximizing the machine’s capabilities and ensuring efficient operation.
Automation and Robotics in VMCs
Automation enhances the capabilities of VMCs:
- Integration with Robotic Systems: Robotic arms can load and unload parts, increasing throughput.
- Benefits of Automation in VMC Operations: Automation reduces labor costs and human error, leading to higher productivity and consistency.
Applications and Benefits of Using a VMC
Diverse Applications of VMCs
VMCs are versatile and find applications in various sectors:
- VMCs in the Automotive Industry: Used for manufacturing engine components, gears, and other parts.
- Aerospace Applications of VMCs: Ideal for creating complex aerospace components that require high precision.
- Role in Consumer Electronics Manufacturing: Used in the production of parts for smartphones, laptops, and other electronics.
Advantages of VMCs Over Other Machining Centers
VMCs offer several benefits:
- Precision and Accuracy: They are capable of achieving tight tolerances.
- Speed and Efficiency: High-speed spindles and quick tool changes reduce cycle times.
- Customization and Flexibility: VMCs can be easily programmed for custom jobs and adjusted for different production runs.
Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Safety in VMC Operations
Regular Maintenance of a VMC
Maintaining a VMC is crucial for its longevity:
- Routine Checks and Maintenance Schedule: Regular maintenance ensures the machine operates at peak efficiency.
- Longevity and Performance Optimization: Preventative maintenance helps avoid unexpected downtime and costly repairs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in VMCs
Common issues might include spindle errors or inaccuracies in machining:
- Identifying and Resolving Operational Problems: Quick troubleshooting can save time and resources.
- Tips from Industry Experts: Experts often share insights on maintaining and troubleshooting VMCs effectively.
Safety Protocols for Operating a VMC
Safety is paramount when operating heavy machinery:
- Essential Safety Measures and Guidelines: Operators should follow strict safety protocols to avoid accidents.
- Training and Safety Compliance in Workplaces: Proper training ensures that operators are aware of all safety measures.
Future Trends and Innovations in VMC Technology
Technological Advances Impacting VMCs
The future of VMCs looks promising with ongoing advancements:
- The Future of Automation in VMCs: Increasing integration with AI and IoT for smarter manufacturing.
- Sustainable Practices and Energy Efficiency: New technologies aim to reduce the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes.
The Global Market and Future Outlook for VMCs
The VMC market continues to evolve:
- Market Trends and Growth Predictions: The demand for more sophisticated VMCs is growing.
- Challenges and Opportunities in the VMC Industry: As technology advances, the industry faces both challenges and opportunities.
Conclusion
Recap of VMC Functionality and Impact
VMCs are integral to modern manufacturing, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility. The continuous improvement in technology promises even greater capabilities in the future.
The Future of Manufacturing with VMCs
With advancements in CNC technology and automation, VMCs are set to revolutionize the manufacturing landscape, making it more efficient, precise, and sustainable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What makes a VMC different from a horizontal machining center? VMCs have a vertically oriented spindle which helps in efficient chip evacuation and is generally preferred for end milling tasks, whereas horizontal centers are favored for jobs requiring heavy material removal.
How do CNC enhancements improve VMC operations? CNC technology enhances the precision and speed of VMC operations, allowing for complex parts to be machined with high accuracy and minimal human intervention.
What are the initial setup requirements for a VMC? Setting up a VMC involves installing the machine, ensuring electrical and fluid connections are properly made, and configuring the CNC system with the necessary software and hardware components.
How can automation in VMCs reduce production times? Automation in VMCs minimizes manual tasks such as tool changes and part loading/unloading, significantly cutting down cycle times and boosting production efficiency.
What safety measures should be observed when operating a VMC? Operators must wear appropriate personal protective equipment, adhere to safety protocols, and undergo regular training to handle VMCs safely.
How frequently should maintenance be performed on a VMC? Preventative maintenance should be conducted according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, typically involving daily, weekly, and monthly checks to ensure optimal performance.